Deploy OpenEMS Backend
1. Debian Linux
This chapter explains how OpenEMS Backend can be deployed on a Debian Linux server. Similar techniques will work for other operating systems as well.
1.1. Prepare operating system environment
| It is recommended to run every service on a server with limited permissions. This example runs OpenEMS Backend with user "root" which is a bad idea for a production server! |
1.1.1. Check JAVA version
Ensure that a JRE version 21 or later is installed. We recommend using temurin-21-jre
For detailed installation instructions, visit Adoptium Installation Guide.
| If you are using an ARM32 device, download temurin-21-jre-armhf_21.0.6+2.deb directly from OpenEMS. |
1.1.2. Create an application directory
Create the directory /opt/openems-backend. This is going to be the place, where we put the JAR file.
Execute mkdir /opt/openems-backend.
1.1.3. Create a config directory
Create the directory /opt/openems-backend/config.d. This is going to be the place, where all the bundle configurations are held.
Execute mkdir /opt/openems-backend/config.d.
1.1.4. Create a systemd service definition
The systemd 'Service Manager' manages system processes in a Debian Linux. We will create a systemd service definition file, so that systemd takes care of managing (starting/restarting/…) the OpenEMS Backend service.
-
Create and open the service definition file.
Execute
nano /etc/systemd/system/openems-backend.service -
Paste the following content:
[Unit] Description=OpenEMS (1) After=network.target (2) [Service] User=root (3) Group=root Type=simple (4) WorkingDirectory=/opt/openems-backend ExecStart=/usr/bin/java -XX:+ExitOnOutOfMemoryError -Dfelix.cm.dir=/opt/openems-backend/config.d -Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism=100 -jar /opt/openems-backend/openems-backend.jar (5) SuccessExitStatus=143 (6) Restart=always (7) RestartSec=10 (8) [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
1 The name of the service. 2 The service is allowed to start after network is available (e.g. to be able to access devices via ethernet connection) 3 It is run as user 'root' to have access to all devices. It is recommended to change this for productive systems. 4 OpenEMS Backend uses a "simple" process fork. 5 The start command. It uses the Java JRE, sets the config directory to /opt/openems-backend/config.d, sets a parallelism value for ForkJoinPool - this depends on the number of OpenEMS Edge devices you expect to connect - and runs the jar file at/opt/openems-backend/openems-backend.jar6 In contrast to what systemd expects, Java exits with status 143 on success. 7 Systemd always tries to restart OpenEMS Backend once it was quit. 8 Systemd waits 10 seconds till the next restart. -
Press Ctrl + x to exit and y to save the file.
-
Activate the service definition:
Execute
systemctl daemon-reload
1.2. Start OpenEMS Backend
To update the OpenEMS JAR file at the target device, it is required to copy the JAR file from your build directory to /opt/openems-backend/openems-backend.jar on the server. Afterwards it is required to restart the systemd service
-
(Re)start OpenEMS systemd service.
Execute
systemctl restart openems-backend --no-block; journalctl -lfu openems-backendThe command restarts the service (systemctl restart openems-backend) while not waiting for the OpenEMS startup notification (--no-block). Then it directly prints the OpenEMS system log (journalctl -lfu openems-backend).
2. Docker
This chapter explains how OpenEMS Backend can be deployed using our official Docker image.
2.1. Prepare system
2.1.3. Setup docker
To setup docker follow the instuctions from docs.docker.com.
2.2. Create a Docker compose
Paste content into a docker-compose.yml
services:
openems_backend:
image: openems/backend:latest
container_name: openems_backend
hostname: openems_backend
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- openems-backend-conf:/var/opt/openems/config:rw
- openems-backend-data:/var/opt/openems/data:rw
ports:
- 8079:8079 # Apache-Felix
- 8081:8081 # Edge-Websocket
- 8082:8082 # UI-Websocket
openems-ui:
image: openems/ui-backend:latest
container_name: openems_ui
hostname: openems_ui
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- openems-ui-conf:/etc/nginx:rw
- openems-ui-log:/var/log/nginx:rw
environment:
- UI_WEBSOCKET=ws://<hostname>:8082 # Change to your actual hostname or ip
ports:
- 80:80
- 443:443
volumes:
openems-backend-conf:
openems-backend-data:
openems-ui-conf:
openems-ui-log:
2.3. Run compose file
To start the previously created docker-compose.yml run the command:
docker compose up -d
2.4. Check logs
To check if the container is up and running, check docker ps:
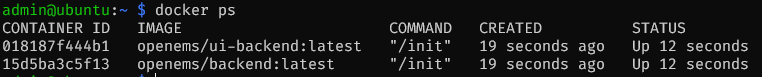
or read its logs with:
docker logs openems_backend
| If you want to run the backend with an InfluxDB instance as well, see: https://github.com/OpenEMS/openems/tree/develop/tools/docker/backend. |